WHAT IS HUNGER?
According to the UN’s Hunger Report, hunger is the term used to define periods when populations are experiencing severe food insecurity—meaning that they go for entire days without eating due to lack of money, lack of access to food, or other resources.
Awareness Generates Action
The Hunger Problem Requires A Little Understanding And A Little Effort. People At Every Level Can Be Made Aware And Any Action Goes A Long Way!
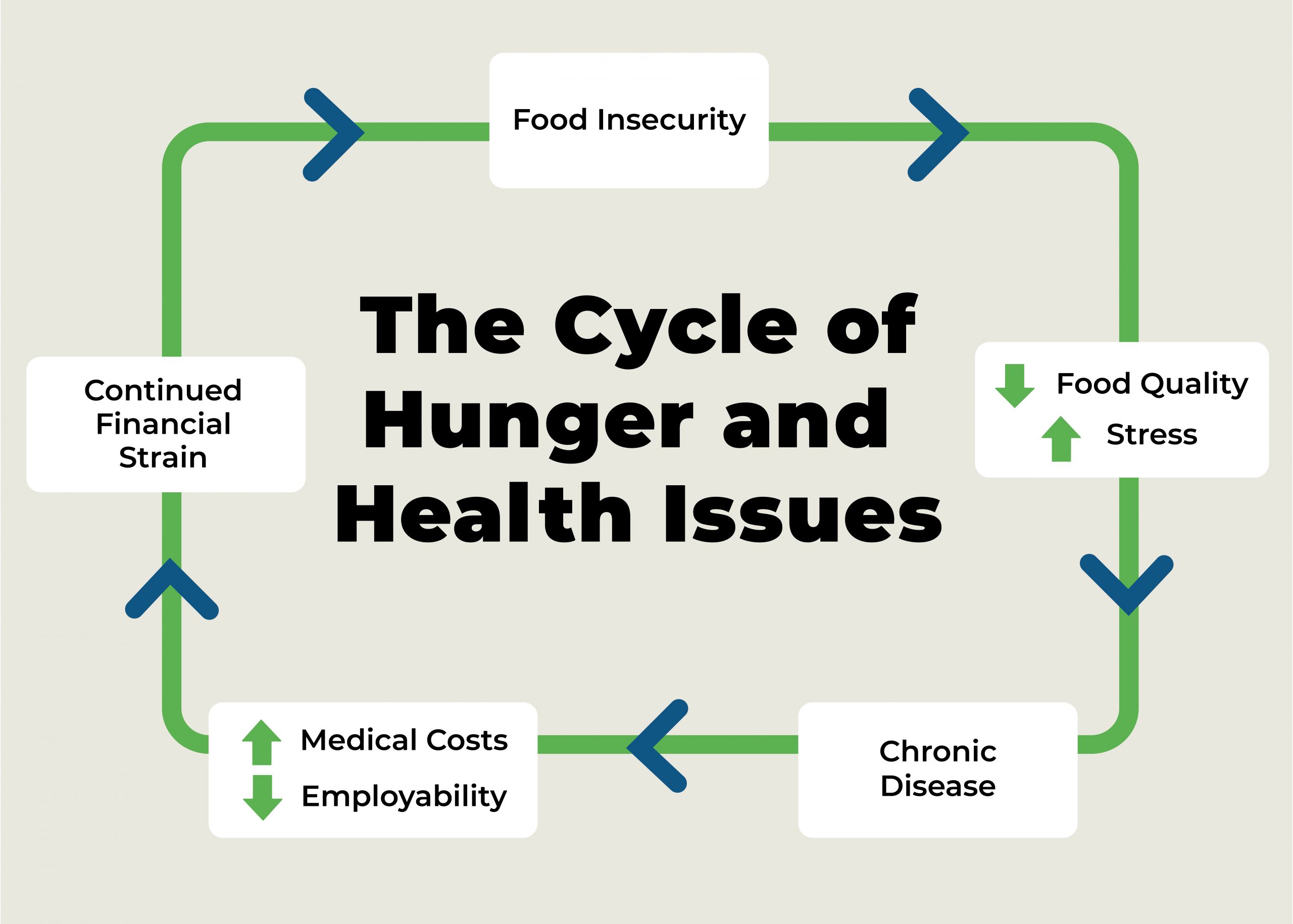
There are many complex and interconnected factors such as poverty, unemployment, food waste, poor infrastructure, unstable markets, climate change, war and conflicts, Nutritional quality, and discrimination that become a cause of hunger both in the United States and abroad despite enough food production.
Demographic Trends
Mounting population and food demands is affected by old production technology and disintegrated community systems to manage requirements for food and reproductive health.


Industrial agriculture
With subsistence farming being displaced, Industrial agriculture affects hunger in developing countries. Farmers managing basic food needs face challenges to find support or opportunities to obtain what they produced for themselves.
A grim number: at the current rate, an additional 2 billion people are expected to face global hunger problems by 2050. Increasing agricultural productivity and sustainable food production are crucial to help change these numbers.
Social inequality
Unfortunately, people with the least social, political or economic power are liable to face hunger or malnutrition. This happens everywhere, in low-income countries, or in marginalized communities in high-income countries.


Education systems
The impact of hunger on education systems is widely underreported.
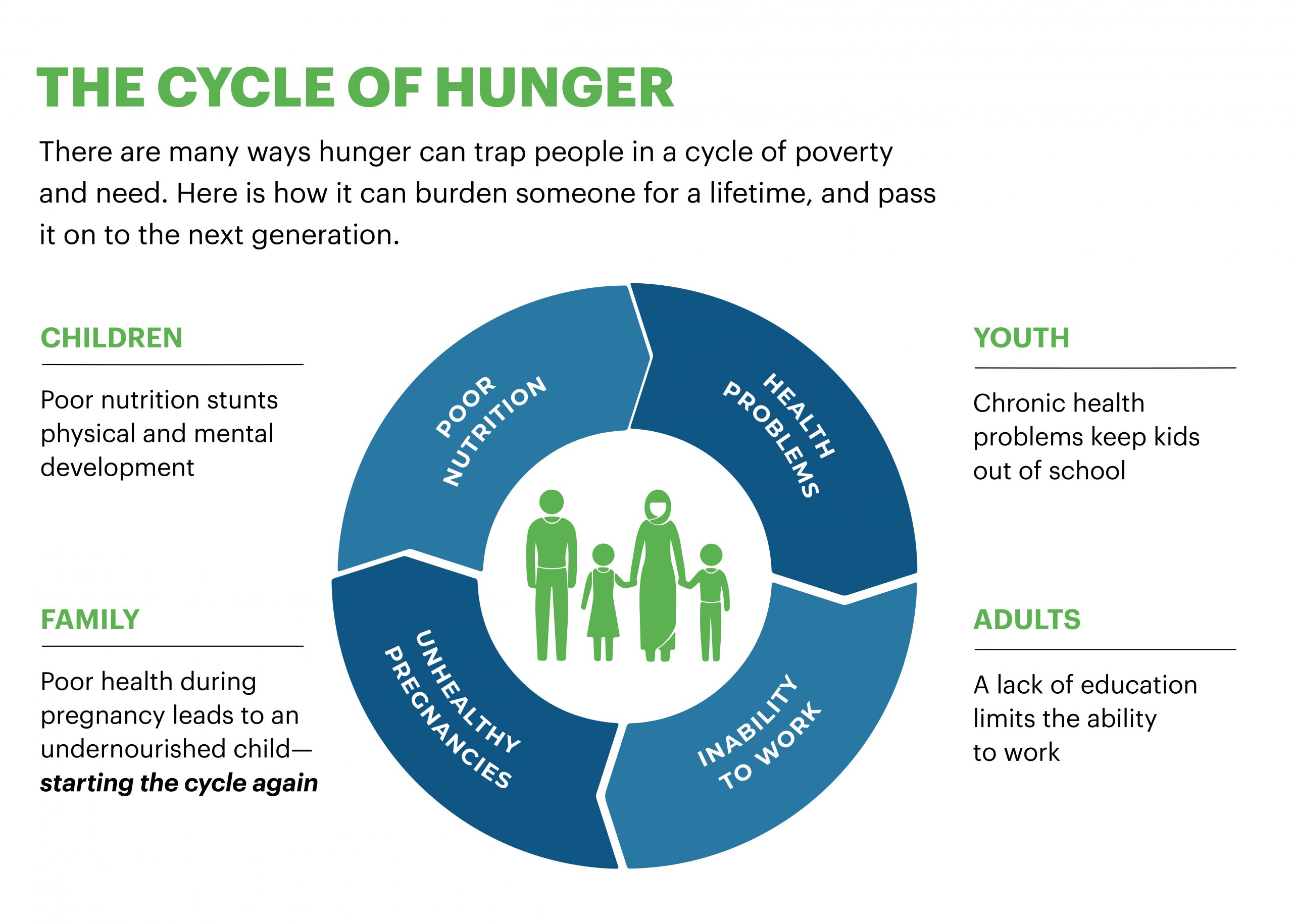
- An estimated 150 million children stay behind in receiving adequate nutrition because of food and hunger, resulting in malnutrition, stunting and disease. Infant mortality requires any efforts to be channeled well.
- Severe malnourishment, to the extent of impacting brain development, is possibly equivalent to the loss of four years of schooling. An estimated 155 million children under the age of five are stunted. Stunting, or impaired growth and development that children experience from poor nutrition and food poverty, impact a child’s cognitive abilities and their performance in school. Astonishingly, stunted children are approximately 20% less likely to read by age eight.
Policy Changes
Policy changes can cause farmers and their families to be displaced, leaving arable and fertile land to not be put in productive use, which is detrimental to poverty and hunger.