The Hunger Problem
WHAT IS HUNGER?
According to the UN’s Hunger Report, hunger is the term used to define periods when populations are experiencing severe food insecurity—meaning that they go for entire days without eating due to lack of money, lack of access to food, or other resources.
Awareness Generates Action
The Hunger Problem Requires A Little Understanding And A Little Effort. People At Every Level Can Be Made Aware And Any Action Goes A Long Way!
Hunger takes on many forms. According to the FAO, while the inflicted may not be “hungry” and have physical discomfort by a high lack of dietary energy, they may still be food insecure. Despite having the means for their food requirements, they may face uncertainty about when they will get access to more food, and may even be forced to ‘get by’ affecting the quality and quantity of the food they have. This food insecurity develops in the short term and long term into dietary deficiencies and has long-term impacts at the individual, community, and country levels.
Hunger and undernourishment severely impact children under five, the worst implications being wasting and stunting. This culminates in high mortality rates and is still challenging many communities. Around 13 million children in the United States live in “food insecure” homes and over 34 million or 10.5% of all American people in the US live in poverty, according to 2019 data from the U.S. Census Bureau. 12 million of those were children. This number is shockingly high for a country of such enormous wealth. This may sound mild, but it means that those households don’t have enough food for every family member to lead a healthy life.
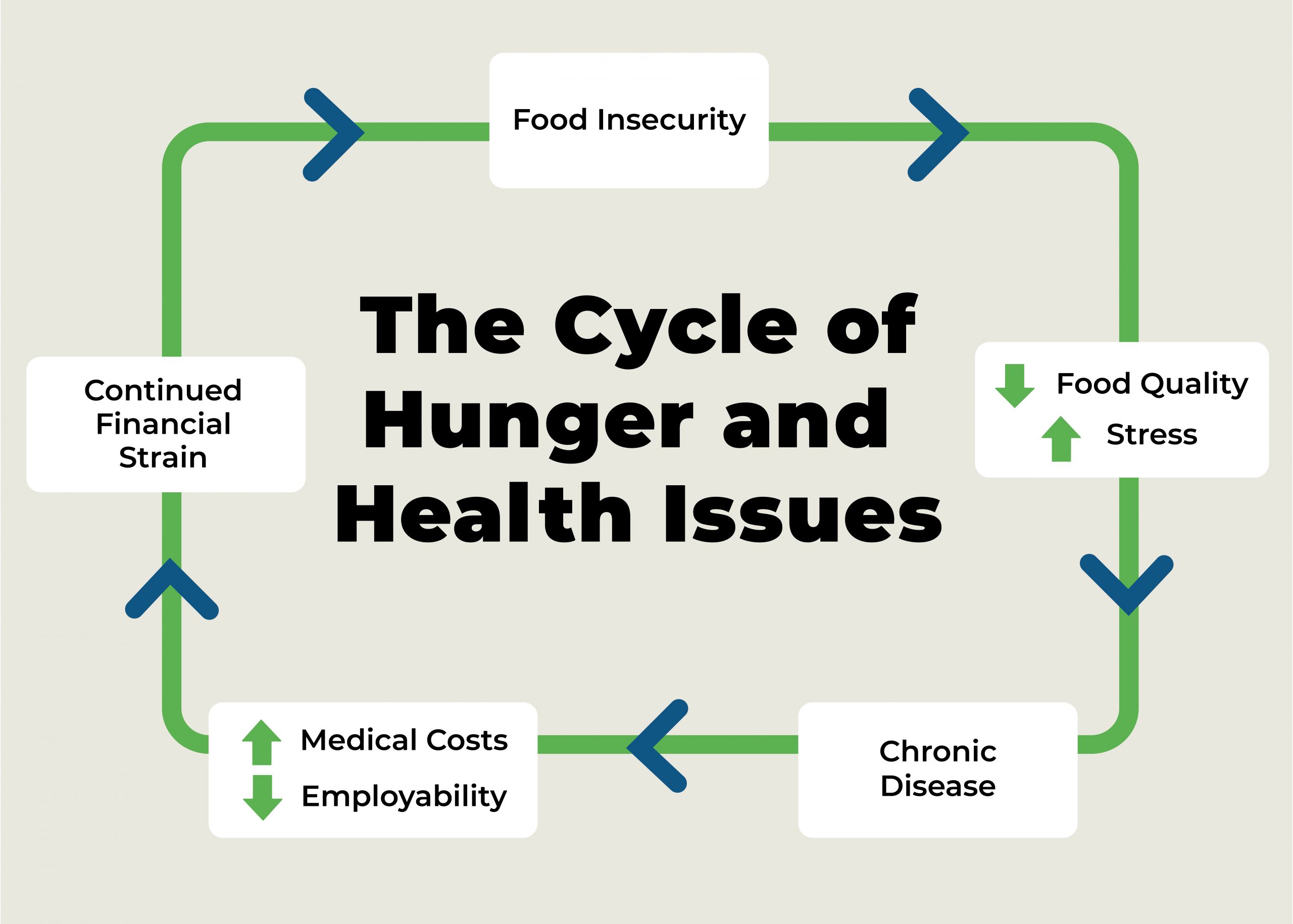
This transcends borders as countries and their import and export needs face challenges when society, and ultimately the country, face the impact of this spin-off.
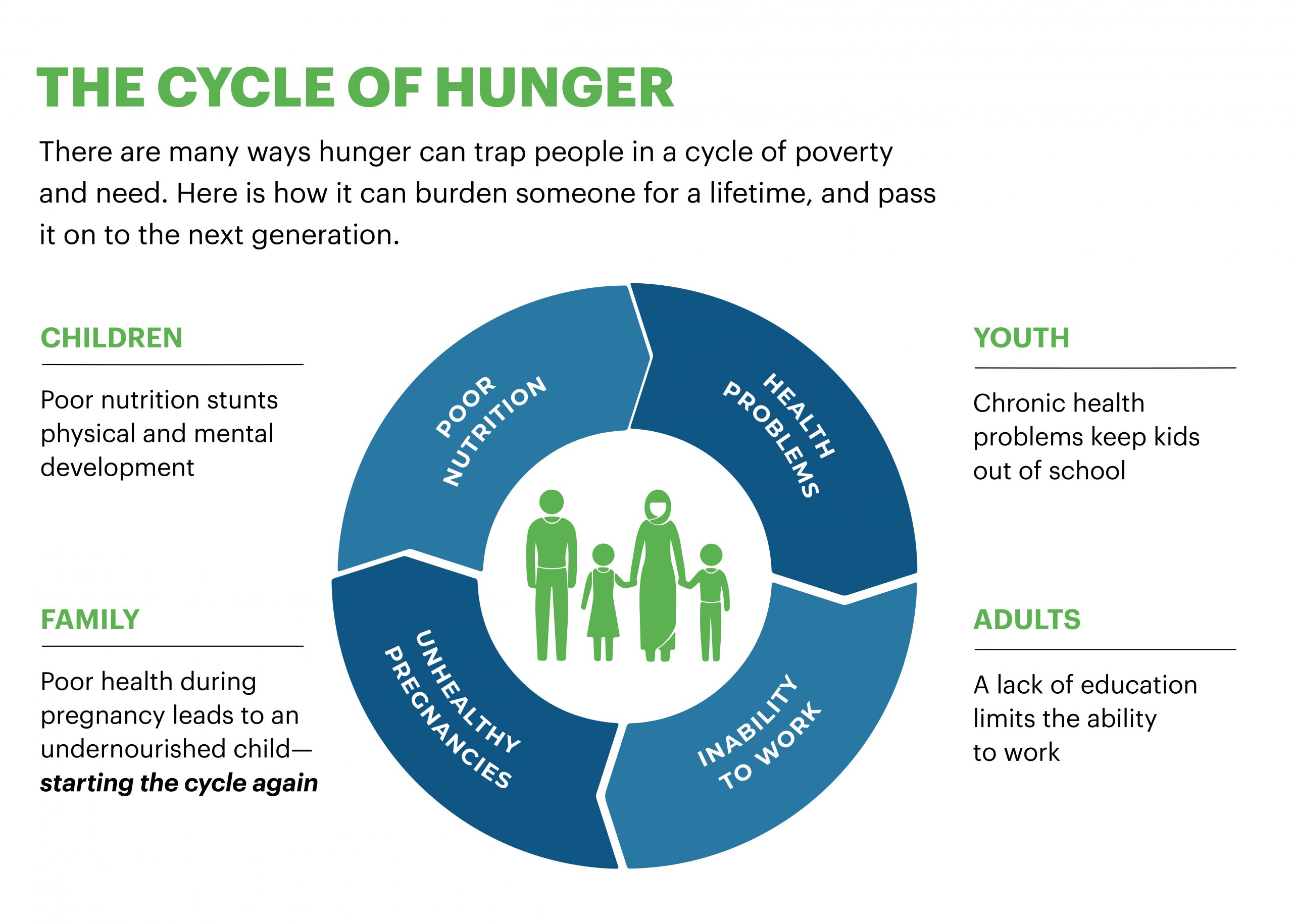
Hunger can trap many people in a cycle of poverty and food insecurity in many ways. If not dealt with, hunger burdens every age for a lifetime, and the effects are passed on to the next generation, which can become trapped in the hunger cycle as well.
Taking on the challenge of world hunger is a critical task because after good decline, the numbers recently started climbing. Globally, close to 811 million people sleep hungry and there are emergency levels of hungry for about 50 million people
Hunger and its impact on the diets of millions with deficiencies nutrition, vitamins and minerals affect the future of communities and entire countries.
Despite enough food produced to for everyone on earth, the UN had to create a goal of a world with zero hunger, in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The multitude of complexities is multifaceted.
